- Lithium is fueling the EV revolution
- Consumer demand is set to triple by 2025
- Lithium is virtually needed in all facets of battery uses, including the sky rocketing demand for EV’s and consumer electronics.
- Friendliest and pro-mining jurisdiction hosting some of the largest lithium reserves on the planet.
- World renowned team responsible for helping build the lithium industry in Argentina as we know it today.
- Untapped potential to unlock one of the greatest spodumene mines on the planet.
Introduction
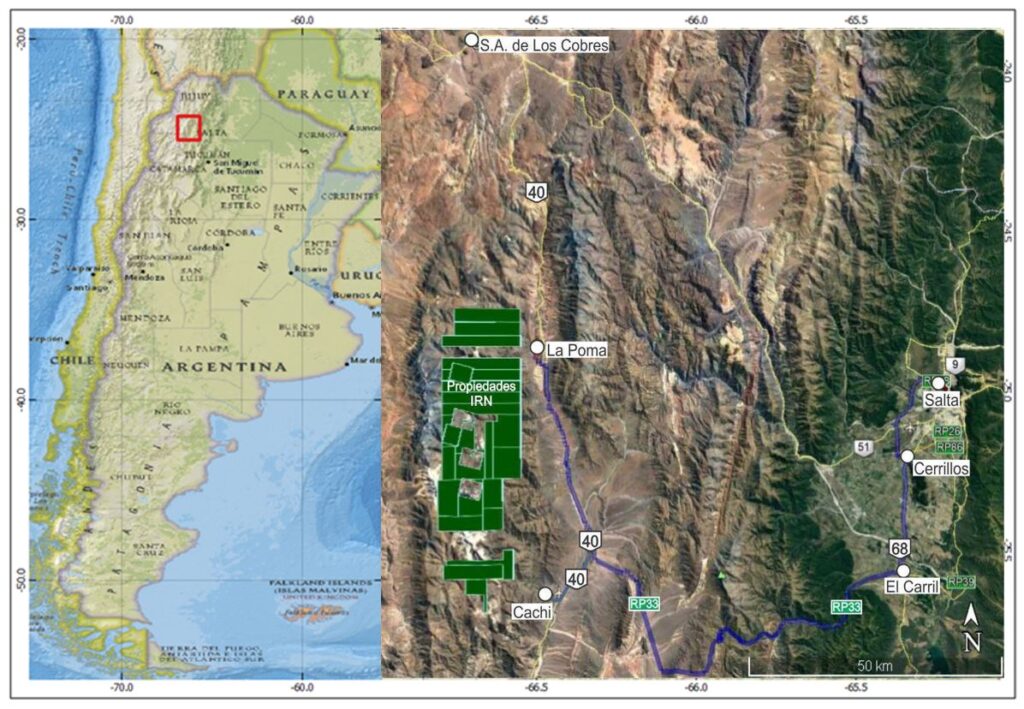
Located in the heart of the lithium triangle South American Lithium owns 50,000+ hectares throughout the El Quemado mining district. The El Quemado project is within one of the finest spodumenic areas in all of Argentina where the potential for mineralization of lithium, columbite-tantalite and rare earth minerals is outstanding.

What Is Lithium?
Lithium is the lightest metal and least dense solid element. It’s high electrochemical potential makes it an extremely valuable component of high energy-density rechargeable batteries.

Lithium Mining
El Quemado has tenements covering 50,000 hectares in the South America region, prospective for lithium mineralization.

Sources
El Quemado
South American Lithium’s Flagship Property
The El Quemado mining project is one of the largest lithium bearing land packages in all of Argentina
The El Quemado mining district is located on the eastern slopes of the Palermo and Cachi Mountains, at an altitude between 3,800 and 4,700 meters above sea level.
It lies Northwest of the town of Palermo Oeste and extends in a N-S belt between the towns of La Poma and Cachi (province of Salta, Argentina), covering an area of over 50,000 Ha.
El Quemado mining district is said to be the most important concentration of Tantalum and Niobium in Argentina. It contains a large number of pegmatitic bodies with large concentrations of niobium, tantalum, lithium and rare earths.

Quebec Claim
The Huaytiquina Project, owned and operated by SALi Lithium Corp, is strategically located in the Salar del Rincón basin, Salta, Argentina. Spanning 7,625 hectares, the project is positioned within the Altiplano-Puna high plateau, a region renowned for its significant lithium resources. With a prime location and access to nearby aquifer systems, the Huaytiquina Project offers exceptional potential for lithium brine extraction and exploration.
The Huaytiquina Project benefits from its proximity to two important aquifer systems: the Catua Aquifer System and the Volcanic Aquifer Complex. These water resources are essential for lithium brine extraction, a critical component of lithium production. SALi Lithium Corp’s access to these water sources ensures that the project is well-positioned to support future extraction activities, contributing to the region’s growing lithium industry.

Rincon Salar
South American Lithium’s Flagship Property
The Huaytiquina Project benefits from its proximity to two important aquifer systems: the Catua Aquifer System and the Volcanic Aquifer Complex. These water resources are essential for lithium brine extraction, a critical component of lithium production. SALi Lithium Corp’s access to these water sources ensures that the project is well-positioned to support future extraction activities, contributing to the region’s growing lithium industry.
SALi Lithium Corp’s Huaytiquina Project is strategically positioned to capitalize on the increasing demand for lithium, driven by the global electric vehicle and renewable energy sectors. With its favorable location, access to water resources, and geological setting, the project offers excellent potential for future lithium brine extraction. SALi Lithium Corp intends to advance exploration activities at Huaytiquina, focusing on defining the resource and evaluating the project’s feasibility for long-term lithium production.
